Chapter 2
Communication and Internet Technologies
2.01 Types and methods of data transmission
Key Term
- Bit – short for binary digit, it is the smallest unit of data in a computer.
- Bit rate – the rate at which data is transferred.
- serial transmission – uses a single wire to transfer bits of data.
- Parallel transmission – uses multiple wires to transfer bits of data.
- Interference – disturbances that can occur in the signals when sending data that may corrupt it.
- simplex transmission – sending data in one direction only at a time.
- Duplex transmission – sending data in both direction at the same time.
- Half-duplex transmission – sending data in both directions but only one direction at a time.
包交换和路由
1. 包交换的概念:
包交换是一种网络传输技术,它将数据拆分成小块(称为“包”或“数据包”),然后将这些包独立地发送到目的地。这些包可以通过网络中的不同路径独立传输,并在目的地重新组装成完整的数据。
2. 包交换的优点:
- 提高网络的利用率:由于包可以通过不同路径独立传输,网络可以更高效地利用可用的带宽。
- 提供更灵活的通信方式:包交换允许同时传输多个数据流,这为多用户共享网络提供了更好的支持。
- 具有容错能力:如果某个包传输失败,只需重新发送该包,而无需重新传输整个数据。
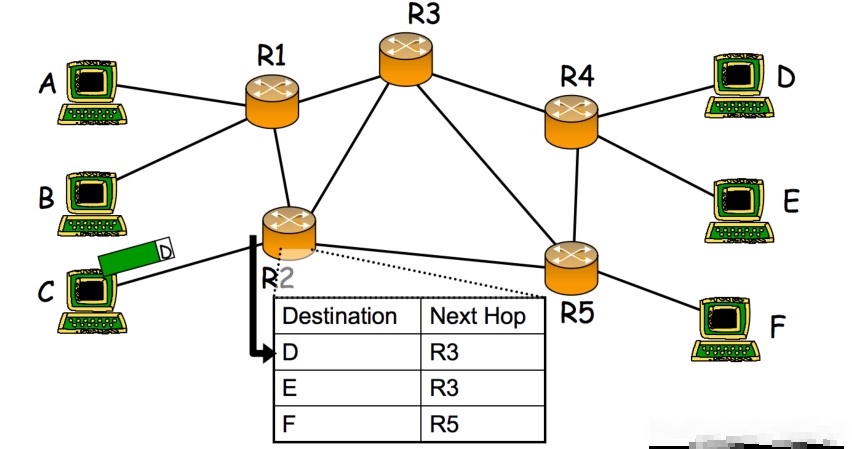
3. 路由的概念:
路由是指在网络中决定包应该按照哪条路径转发的过程。每个网络节点(例如路由器)都会根据目的地址来选择一个合适的出口接口,并将包转发到下一个节点。
4. 路由的作用:
- 确保包能够通过合适的路径到达目的地:路由器根据目的地址来进行转发决策,以确保包能够正确地到达目标设备或网络。
- 优化网络性能:通过选择最佳路径和避免网络拥塞,路由器能够提高网络的性能和效率。
- 确保网络的可靠性和冗余:通过使用多个路径和备用路由,路由器能够提供冗余和容错能力,以确保即使某个路径故障,数据仍然能够进行正常传输。
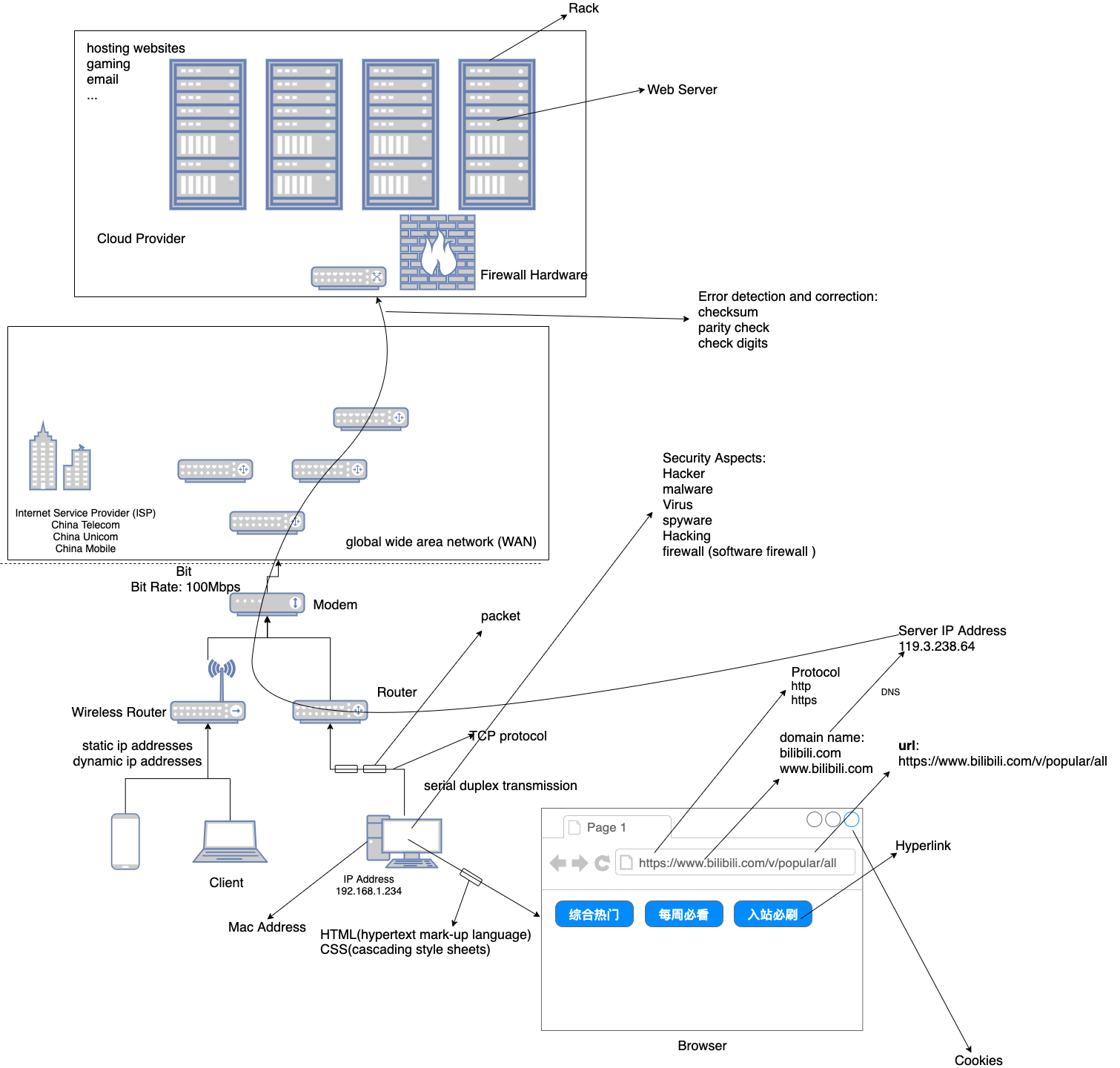
Data packets
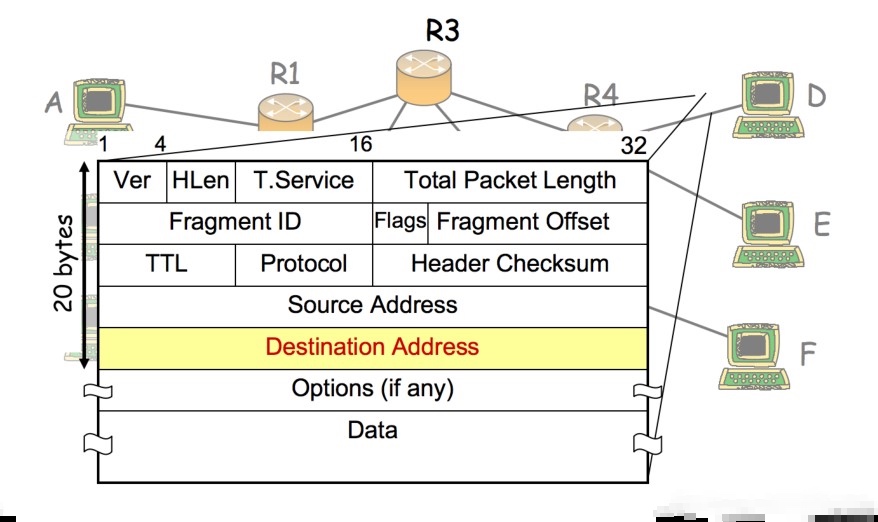
Data is broken up into packets before it is transmitted. Data packets are split up into::
- packet header
- IP address of the sending station and receiving station
- the sequence number of the packet(it can be reassembled)
- packet size(ensure the receiving station knows that the whole packet has been received)
- payload (the actual data)
- packet trailer
- cyclic redundancy check (CRC) (error check)
- a way of identifying the end of the data packet
Data packets allow data to be sent in manageable chunks that can be sent along the most efficient route from A to B
Routers (known as nodes) are used to control the path a data packet takes from sending station to receiving station.
packet switching, each data packet can take a different route; each route taken is independent of each other.
Benefits of packet switching
- There is no need to tie up a single communication line.
- It is possible to overcome failed, busy or faulty lines by simply rerouting packets.
- It is relatively easy to expand package usage.
- A high data transmission rate is possible.
Drawbacks of packet switching
- Packets can be lost and need to be re-sent.
- The method doesn’t work well with real-time streaming (for example, a live sporting event being transmitted over the internet).
- There is a delay at the destination whilst the packets are being reordered.
串行传输和并行传输
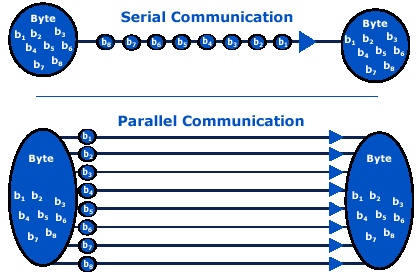
串行传输:将组成字符的各位串行依次地传输,使用一根数据线传输数据,一次传输1个比特,多个比特需要一个接一个依次传输;在串行传输中又分为同步传输和异步传输。
并行传输:字符编码的各位(比特)同时传输,也就是使用多根并行的数据线一次同时传输多个比特。
常见的并行和串行接口

并行接口 - PATA,Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment,并行高级技术附件接口,可用于连接硬盘、光驱、连接打印机、扫描仪等。 (早期硬盘传输技术,已经被SATA替代)
串行接口 - SATA,Serial ATA接口 (硬盘接口,消费级硬盘)

并行接口 - 并口,Parallel Port (一般用于连接打印机、扫描仪等,对应串口)
并行接口 - COM串行口(老式鼠标接口,已经被USB代替)
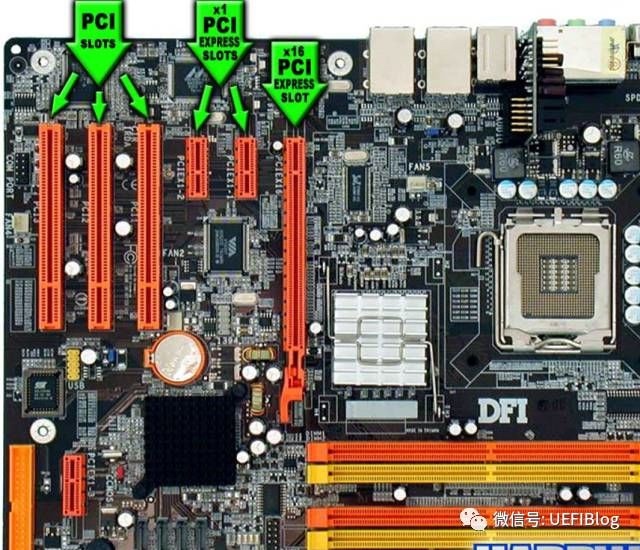
并行接口 - PCI,Peripheral Component Interconnect,外设部件互连接口,用于插接外置网卡、声卡、显卡和调制解调器卡等。(并行数据总线, 老式显卡使用PCI,现在都使用PCIE接口)
串行接口 - PCI Express,PCI E接口 (串行数据总线)

串行接口 - USB接口
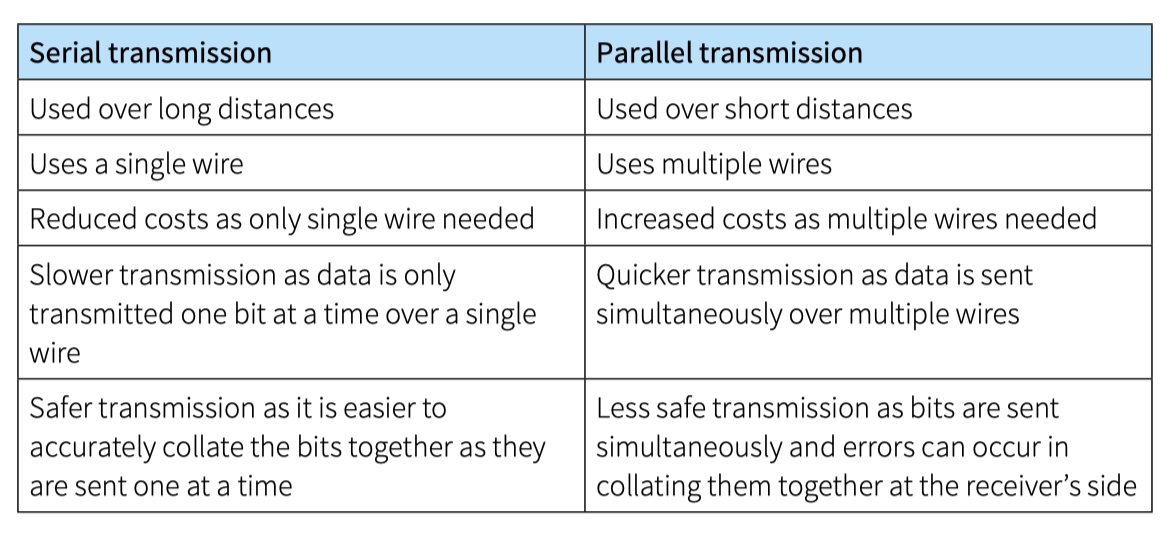
串行传输和并行传输的优缺点
从原理上讲,在相同的工作频率下并行传输的传输速度远比串行传输大,但并行线路有一些难以克服的缺点,导致依靠并行线路的并行传输无法用于长距离通信。计算机与外界的长距离通信,例如与网络中的另外一台计算机进行通信时,只能使用串行传输。串行传输方式大有彻底取代并行传输方式的势头。SATA取代PATA,USB取代Parallel Port,PCI E取代PCI接口。
并行传输的优缺点:
成本高,并行传输如果每个时钟节拍发送多少个比特,则需要多少数据线(另外还需要多根控制线)。
PATA(并行传输)连接线缆包含40根导线(16根数据线,24根用于接地和进行控制);SATA(串行传输)连接线缆包含7根导线(4数据线+3接地线)。如果长距离通信,从成本上来讲,并行通信是串行通信的数倍。
并行接口占用空间大,对应线缆多占用空间也会大。
信号线之间的干扰大,不能用于长距离传输。并行线路多,线路间会产生干扰。并排的信号线在进行高速传输时,会在每条信号线的周围产生微弱的电磁场,出现串音干扰,进而影响到其它信号线中的数据传输。传输距离越长,串音干扰越严重。
PATA线缆的长度不能超过0.4米,而SATA线缆可以达到1米。
并行传输只适合于短距离、要求传输速度快的场合使用。
传输频率低,如果传输频率高的话,数据线之间会产生很大的干扰,造成数据出错,即使为数据线添加屏蔽层,也不能保证屏蔽掉高频率产生的干扰。所以,并行传输的最高传输频率有一定限制。
Serial data transmission
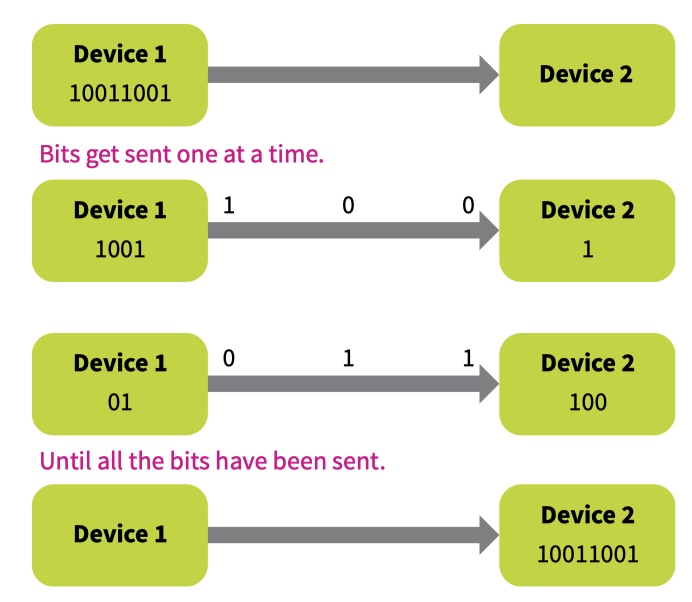
serial transmission uses a single wire to transfer the data bits.
A single wire is cheap to build and can transmit data over long distances.
a 56K modem can transmit 57 600 bits per second.
Parallel data transmission
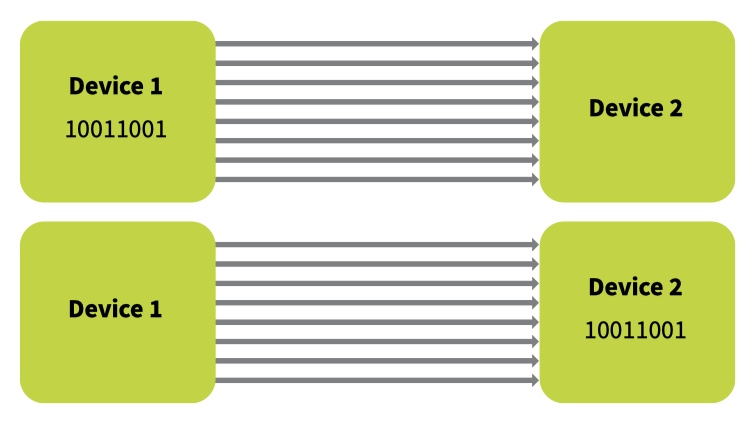
Parallel transmission uses several wires to transfer the data bits simultaneously.
Parallel transmission transfers data quicker than serial transmission.However, because there are more cables, parallel transmission is more expensive and is therefore limited to shorter distances.
Parallel transmission is quite simple to implement but, because it has multiple wires, interference can occur between them.
parallel transmission is generally limited to short distances of around 5 metres. Serial transmission is up to 100 metres.
For many years, parallel transmission was used for data transfer between computers and printers.
Today, parallel transmission has largely been replaced by high-speed serial transmission methods such as the Universal Serial Bus (USB), which transmits data much quicker than parallel transmission.
Parallel transmission is still sometimes used in simple computers such as integrated circuits (IC) where low costs, simplicity and speed are important factors.
单工通信、半双工通信、全双工通信
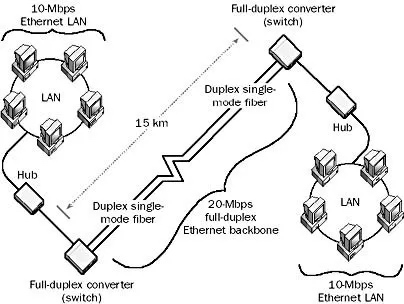
单工数据传输只支持数据在一个方向上传输;在同一时间只有一方能接受或发送信息,不能实现双向通信,举例:电视,广播。
半双工数据传输允许数据在两个方向上传输,但是,在某一时刻,只允许数据在一个方向上传输,它实际上是一种切换方向的单工通信;在同一时间只可以有一方接受或发送信息,可以实现双向通信。举例:对讲机。
全双工数据通信允许数据同时在两个方向上传输,因此,全双工通信是两个单工通信方式的结合,它要求发送设备和接收设备都有独立的接收和发送能力;在同一时间可以同时接受和发送信息,实现双向通信,举例:电话通信。
网卡的全双工(Full Duplex)是指网卡在发送数据的同时也能够接收数据,两者同步进行。这好像我们平时打电话一样,说话的同时也能够听到对方的声音,目前的网卡一般都支持全双工。
Hub(集线器) - 半双工 Switch(交换机) - 全双工 Router(路由器) - 全双工
Simplex transmission (单工通信)
In simplex transmissions data is sent in one direction only.
An example is a television broadcast, where data is transmitted to receiving televisions.
Full duplex transmission (全双工通信)
In full duplex transmissions data is sent in both directions at the same time.
An example is a telephone conversation where both people can speak to each other at the same time.
Half-duplex transmission (半双工通信)
In half-duplex transmissions data is sent in both directions but only one direction at a time.
An example is a walkie-talkie (two-way radio):: both people can speak to each other but only one person can speak at a time.
Different methods of data transmission can be combined. For example, a modern network uses serial duplex transmission whereas a walkie-talkie uses serial half-duplex transmission. A mouse uses serial simplex transmission. You can also get parallel simplex, parallel duplex and parallel half-duplex transmissions too.
USB
universal serial bus (USB-A) is a form of serial data transmission. It is the industry standard.
- the computer automatically detects the device
- the device is automatically recognised and the appropriate device driver is loaded.
USB benefits
- Devices plugged into the computer are automatically detected and device drivers are automatically loaded up.
- Connections can only fit one way preventing incorrect connections being made.
- Has become an industry standard.
- Can support different data transmission rates.
- No need for external power source since cable supplies +5 V power. USB protocol notifies the transmitter to re-transmit data if any errors are detected.
- Relatively easy to add more USB ports if necessary by using USB hubs.
- Backward compatible.
USB drawbacks
- Standard USB only supports a maximum cable length of 5 m; beyond that, USB hubs are needed to extend the cable length.
- Even though USB is backward compatible, very early USB standards (V1) may not always be supported by the latest computers.
- Even the latest version 3 (V3) and version 4 (V4) USB-C systems have a data transfer rate which is slow compared with, for example, Ethernet connections.
2.02 Methods of error detection
The need to check for errors
When data is transferred there is always a risk that the data may be corrupted, lost or even gained.
Errors can occur during data transmission due to::
- electrical interference – can corrupt data
- packet switching – can lead to data being lost or out of synchronisation
- skewing of data – bits arrive at their destination no longer synchronised.
Error detection and correction
Errors can occur when transmitting and storing data
checksum
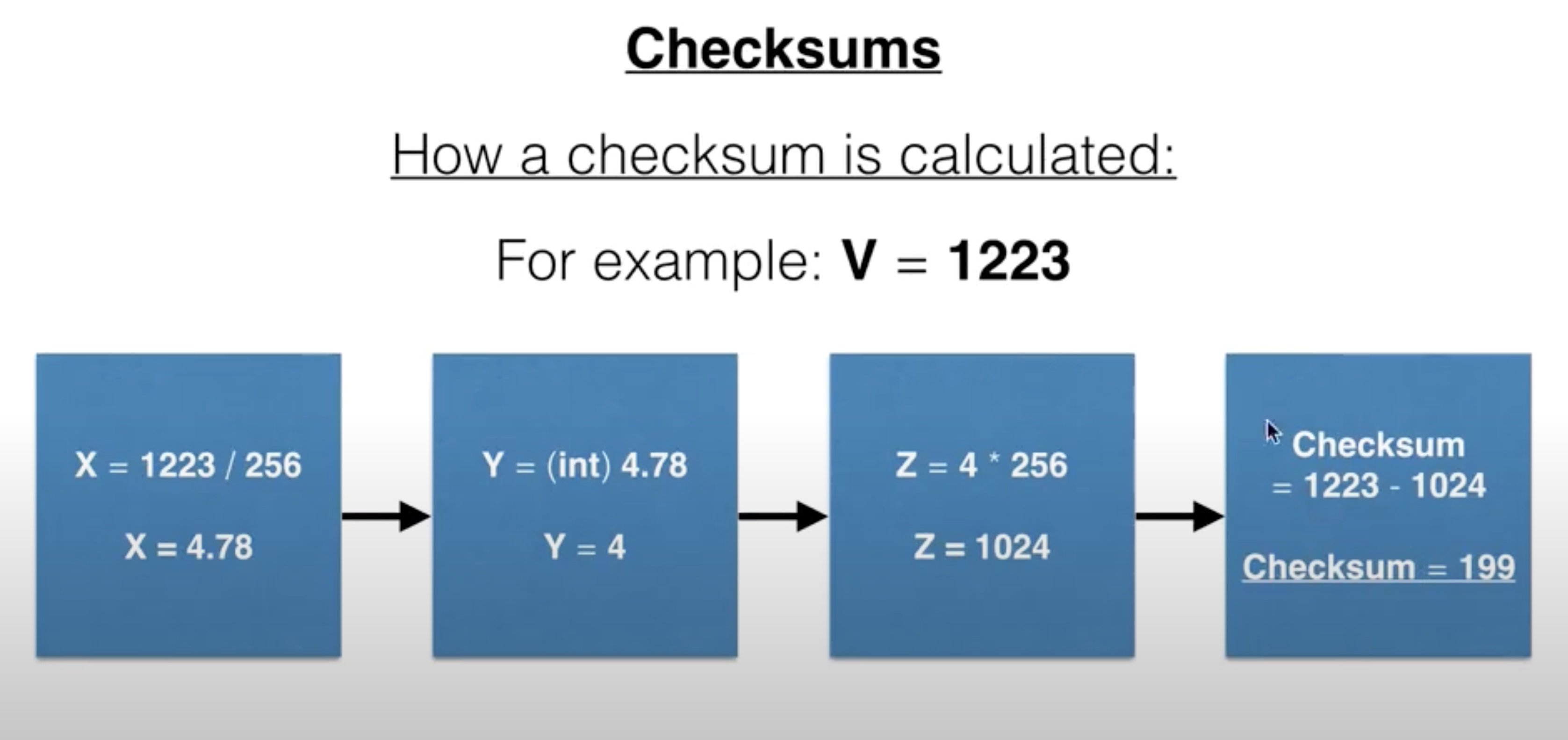
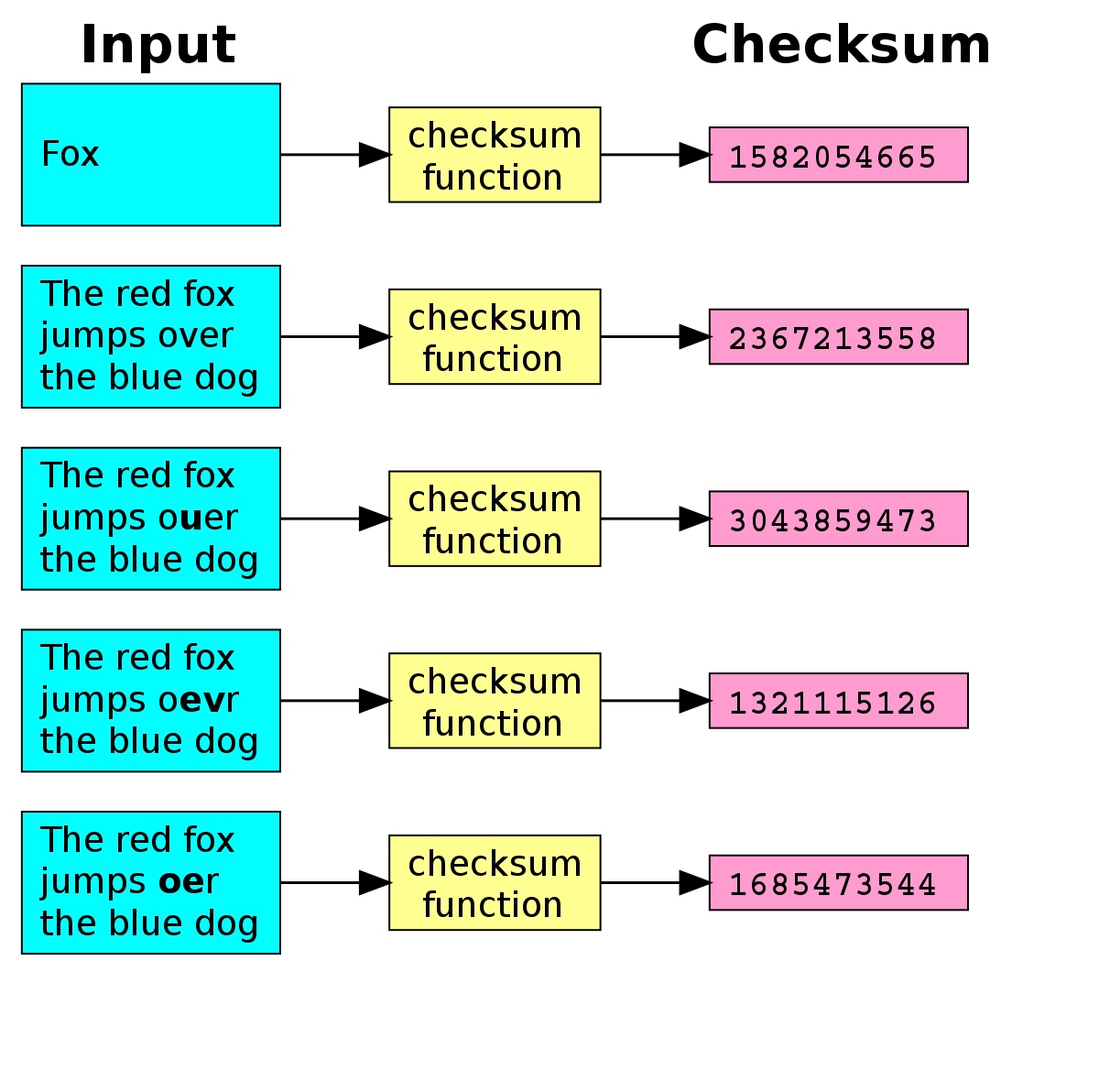
A checksum is a simple method of error detection. The number of bits being transmitted is counted up and this numeric count is transmitted with the data. The receiver can then see if the same number of bits has arrived.
在一些网站上下载文件的时候可以看到Checksum这种东西,用于对下载文件的完整性进行校验。比如在Apache POI上下载就会提供完整的校验文件。
Parity check
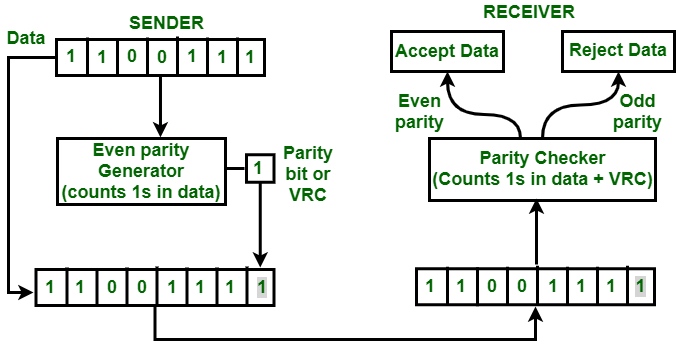
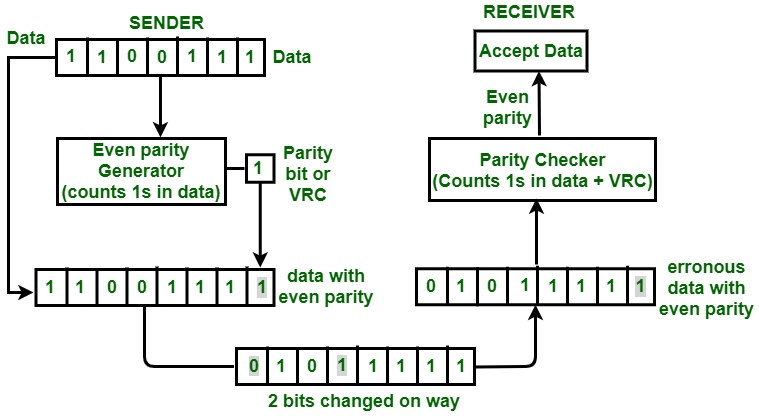
A parity check uses a parity bit to make sure that that the data has been sent accurately.
Parity can be even (even number of 1-bits) or odd (odd number of 1-bits). The left-most bit is reserved for a parity bit.
Parity blocks can be used to determine exactly which bit has been corrupted or changed following data transmission.
The devices that the data is being transferred between will be set to check for even parity or odd parity before the data is sent.
echo check
An echo check requires data to be sent back to the sending computer where it is compared with the data originally sent.
if the two sets of data are different, it is not known whether the error occurred when sending the data originally or if the error occurred when sending the data back for checking.
Drawback of echo checks::
- If the two sets of data are different you will have no way of knowing whether the error occurred when originally sent, or when it was sent back
- Echo checks require a lot of extra data to be transmitted
check digits
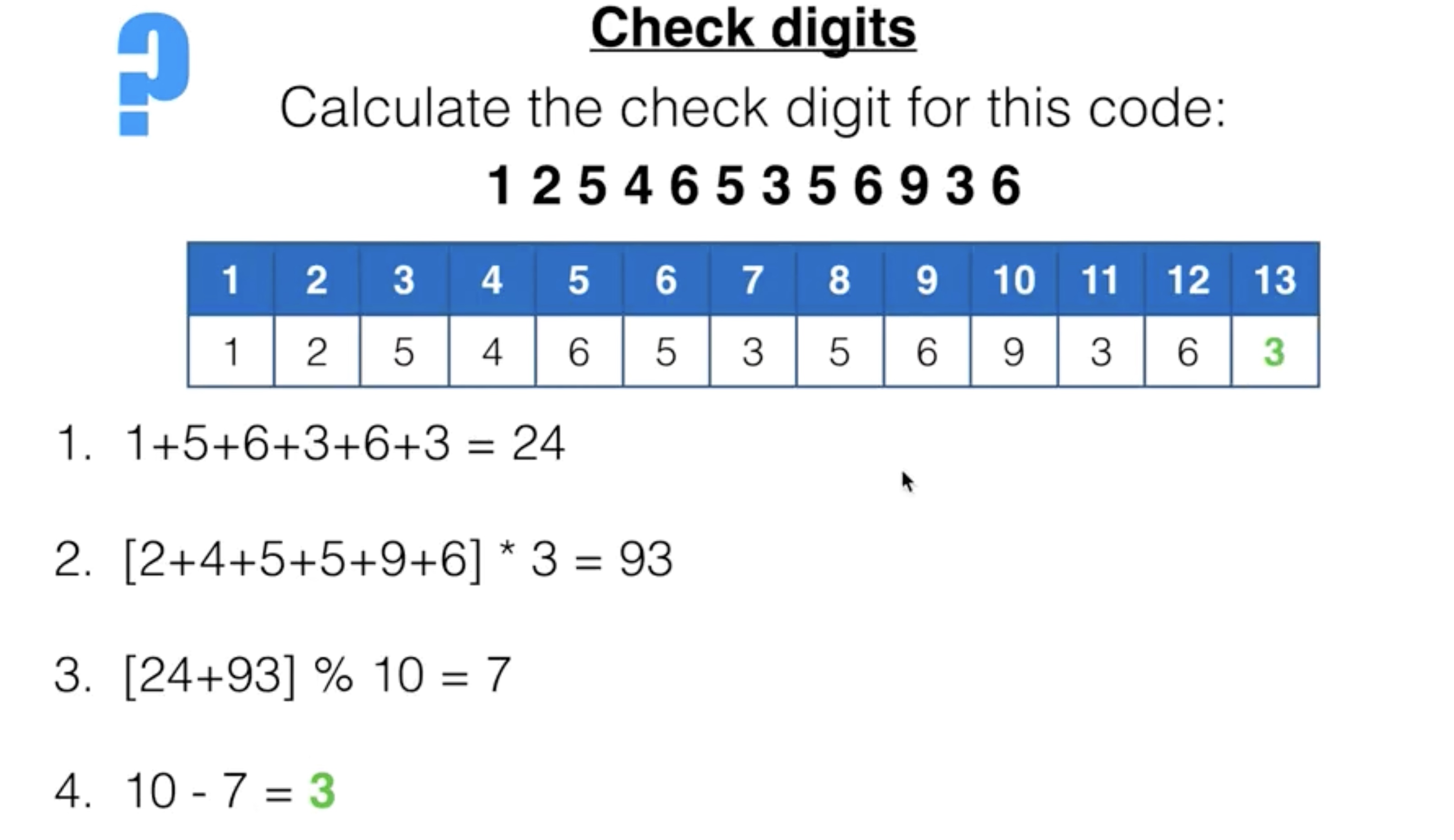
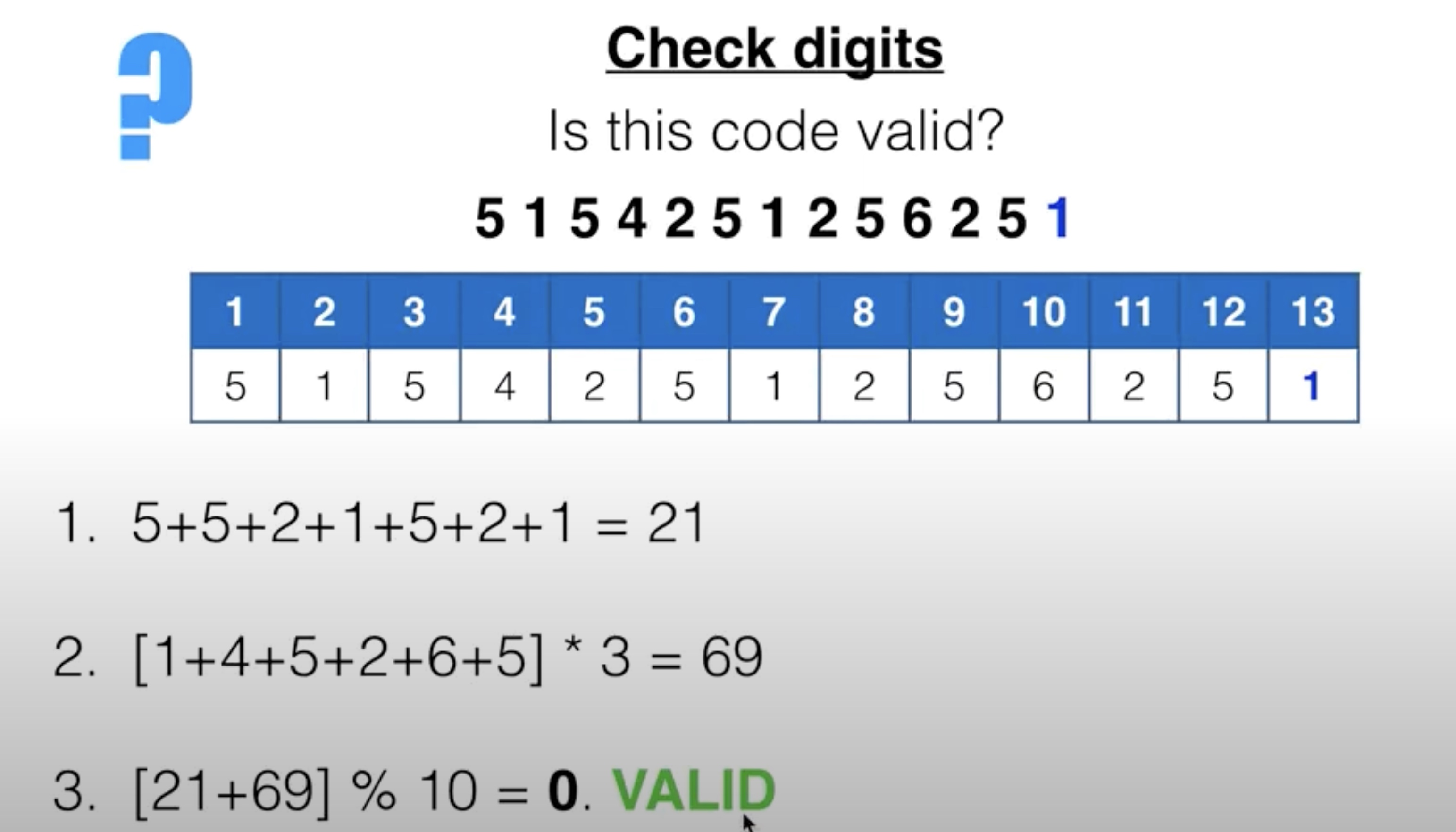
A check digit is a method of error detection that is used on identification numbers such as barcodes, ISBNs and bank account numbers.
Check digits can detect::
- incorrect digits entered
- transposition errors
- omitted or extra digits in the number
- phonetic errors (for example, 13 (thirteen) instead of 30 (thirty)).
automatic repeat request (ARQ)
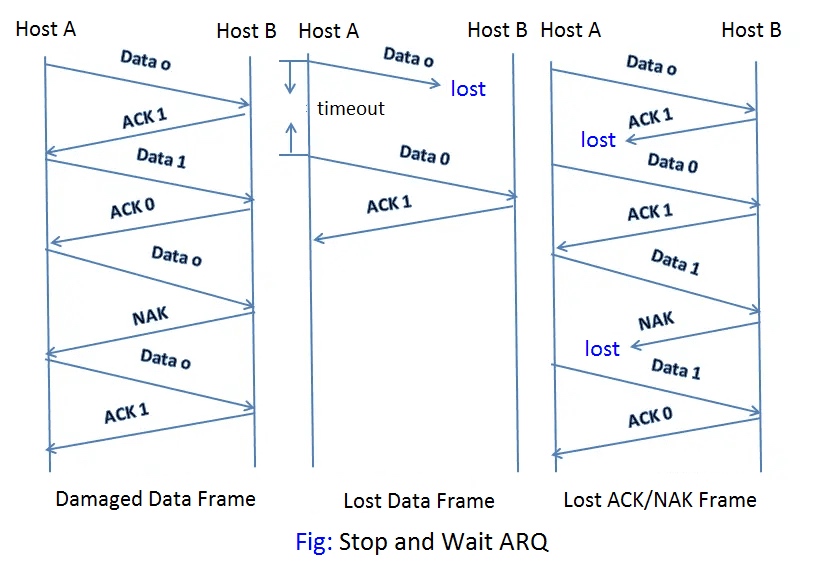
ARQ的概念: 自动重传请求(ARQ)是一种通信协议,用于在数据传输中检测和纠正错误。它基于发送方和接收方之间的确认和重传机制,以确保数据的可靠传输。
ARQ如何工作: ARQ使用以下步骤来实现可靠的数据传输: a. 发送方将数据划分为一系列的数据包,并按顺序发送这些包。
b. 接收方收到数据包后,会对其进行校验,以检测是否有任何错误。
c. 如果数据包在传输过程中没有错误,接收方会发送确认(ACK)给发送方,表示顺利接收。
d. 如果数据包在传输过程中有错误,接收方发送否定确认(NAK)给发送方,表示需要重新发送数据包。
e. 发送方接收到NAK后,会重新发送有问题的数据包。
f. 这个过程会一直进行,直到接收方收到所有正确的数据包,并按正确顺序重新组装数据。
- ARQ的优点:
- 可靠性:ARQ提供了一种可靠的数据传输机制,通过检测和纠正错误,确保数据的正确性。
- 冗余检测:ARQ使用校验和等技术来检测数据包中的错误,以便及时发现并进行重发。
- 自适应:ARQ根据网络状况自动调整重传的速率和方式,以提高数据传输的效率。
- ARQ的局限性: 虽然ARQ是一种可靠的数据传输机制,但它也有一些局限性:
- 增加延迟:由于需要进行确认和重传,ARQ会引入额外的延迟,特别是在有较高丢包率的网络环境中。
- 额外的开销:ARQ需要使用额外的带宽和处理能力来发送和接收确认信号,增加了网络资源的消耗。
Automatic repeat request (ARQ) is a set of rules for error control when transmitting data. It is often used by mobile phone networks to guarantee data integrity.
When the device receiving the data detects there is an error with a packet, it automatically sends a request to the device transmitting the data to resend the packet. This resend request will be sent repeatedly until the packet is received error free or a limited amount of resend requests is reached.
2.03 Symmetric and asymmetric encryption
Key Term
- plaintext – original data
- ciphertext - encrypted data
密码的来源
密码的产生(第一回合)

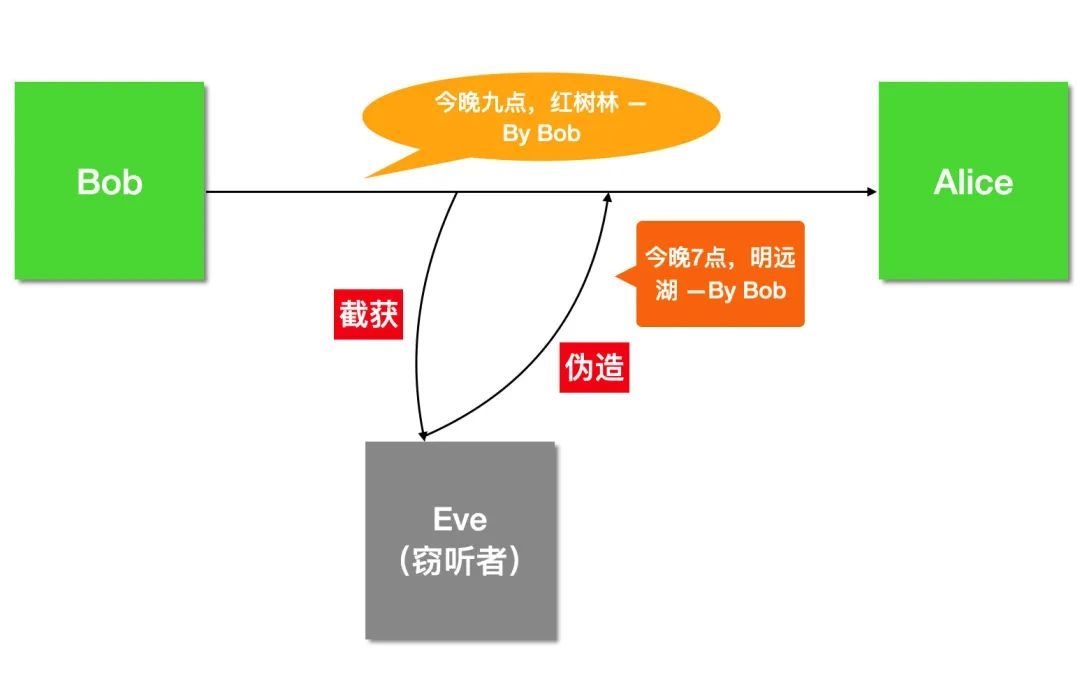
Alice 和 Bob,以及窃听者代表 Eve。
我们从 Alice、Bob 约会的故事展开,来讲讲其中暗藏着哪些危机,又是如何一步步化解的
九月,一个夜黑风高的晚上,Bob 想约 Alice 出来玩,于是给 Alice 发了一封邮件
但我们都知道网络是不可信的,并且由于消息在网络中是明文传输的,所以黑客可以轻易的截获、篡改甚至冒充Bob。
黑客窃听伪造
瞧,Eve 轻易的拿到了邮件内容 (窃听),并且修改了邮件内容 (篡改),甚至说他可以随时冒充 Bob 给 Alice 发送邮件 (伪装)。
如果上图中 Eve 伪造的内容被 Alice 接收到了,那么后果可想而知。
现实世界中,我们每天都在通过网络进行聊天、转账、浏览不存在网站。
如果都是这样明文传输数据,显然毫无安全感。
第二回合
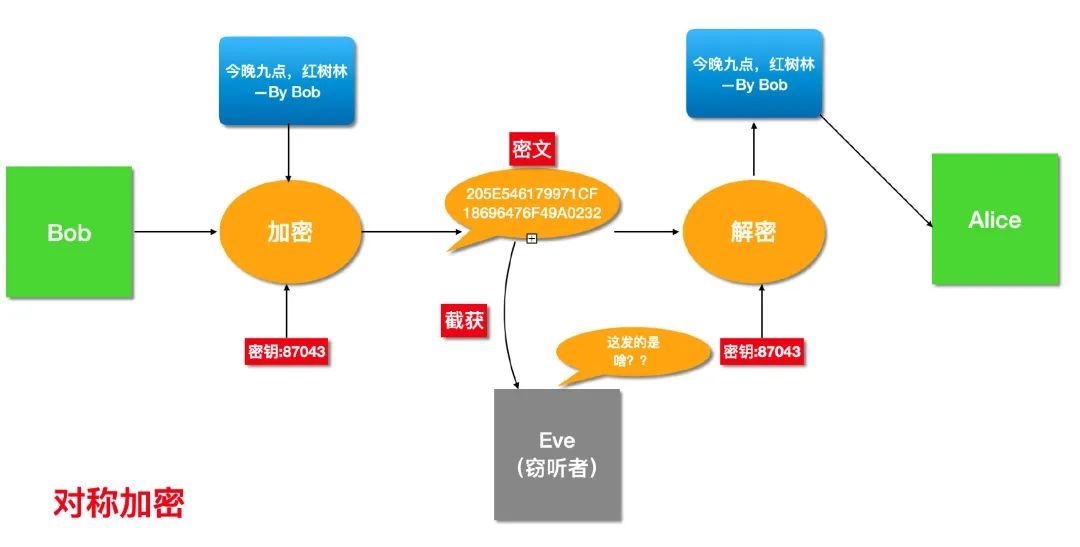
既然我们不能明文传输,那么 Bob 和 Alice 提前商量好密钥,使用对称加密对邮件内容加密不就好了~
只要 Bob 和 Alice 能够保证 密钥不泄露,整个通信就是安全的。
如果密钥泄露,被中间人截获,那么就等同于明文通信。
所以我们不能把安全性寄托在人上面。
并且这里也存在一个问题,如果两个人不能线下见面, 如何在网上安全的交换密钥呢?
这似乎是无解的,因为交换密钥的时候我们必须明文通信,不然对方根本看不懂。但是明文交换即意味着可能泄露。
但是别忘了我们的密码学工具箱里还有一个好东西— 「非对称加密」。
Bob 和 Alice 各自生成一对公私钥,因为公钥本来就是公开的,即可以被任何人获取,所以可以通过网络明文交换公钥。
然后使用公钥加密邮件内容后发送给对方,接收者使用自己的私钥即可解密。完美~
第三回合
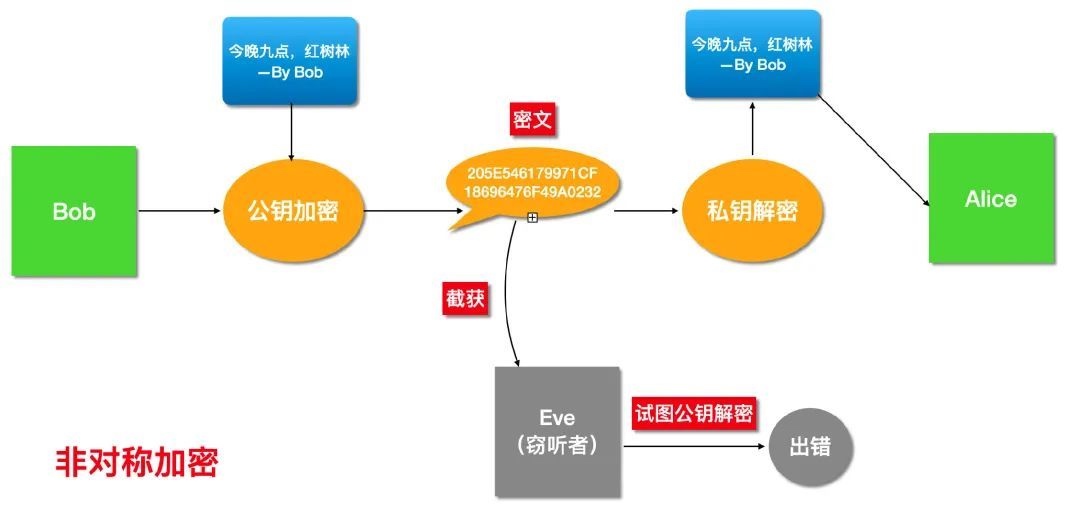
在非对称加密体系下,Bob 如何给 Alice 发消息的。
首先 Alice 需要先生成一对公私钥,私钥只能 Alice 自己知道,公钥是可以让任何人都知道的,因此可将公钥直接发送给 Bob,就算被截获也无所谓。
非对称加密
Bob 使用 Alice 的公钥加密邮件内容,加密后的内容只能由 Alice 的私钥解密,所以就算 Eve 截获也是徒劳。
反之,如果 Alice 想给 Bob 回信,就需要用 Bob 的公钥加密后发送。
这就解决了密钥交换问题,也保证了邮件内容不会泄露。也就是说现在可以防窃听。
如何证明Bob是Bob
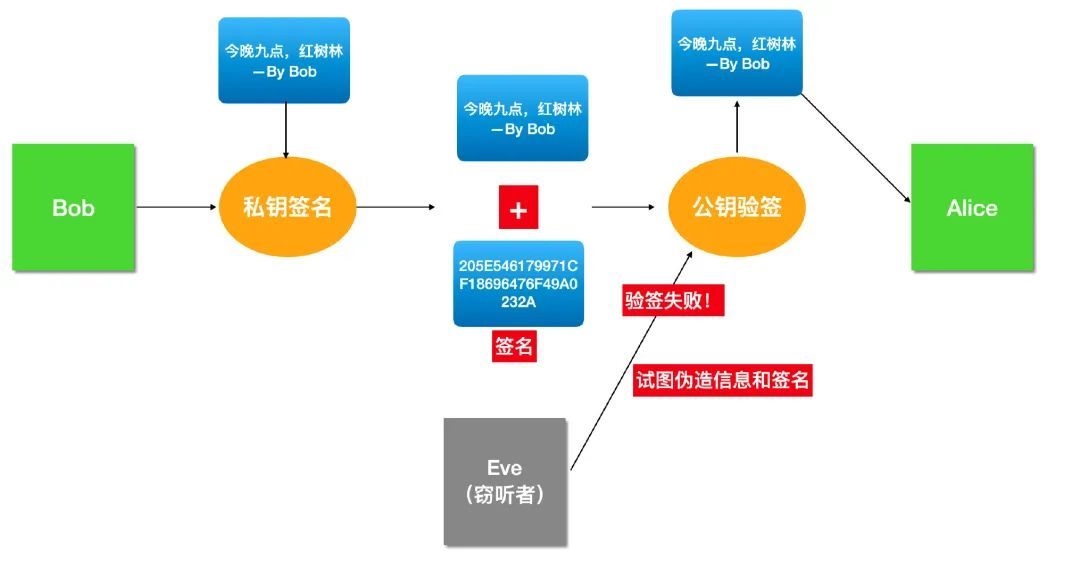
Eve 也可以使用 Alice 的公钥冒充 Bob 给 Alice 发邮件啊,因为 Alice 的公钥本来就是公开的,任何人都可以获得。
由于 Eve 也可以获得 Alice 公钥,所以没法防止 Eve 伪造和篡改,并且对于 Alice 而言,她无法分辨出邮件到底是 Eve 发的还是 Bob。
所以这个问题的本质就是 「Alice 如何确认邮件来自于 Bob」。
所以我们需要在计算机中引入类似的机制:
即只有 Bob 自己能够产生的独一无二的标志,并且其它人能够验证这个标志确实是属于 Bob的。
这就是「数字签名」。
就是 Bob 自己的私钥,Bob 用自己的私钥对邮件内容计算一个「签名」,将「签名」和邮件内容一起发送出去,接受者 Alice 可以使用 Bob 的公钥验证这个签名是否正确,这就叫「验签」。
如果不是 Bob 的私钥计算的签名,那么 Alice 用 Bob 公钥验签将会出错。
如何证明我就是我?
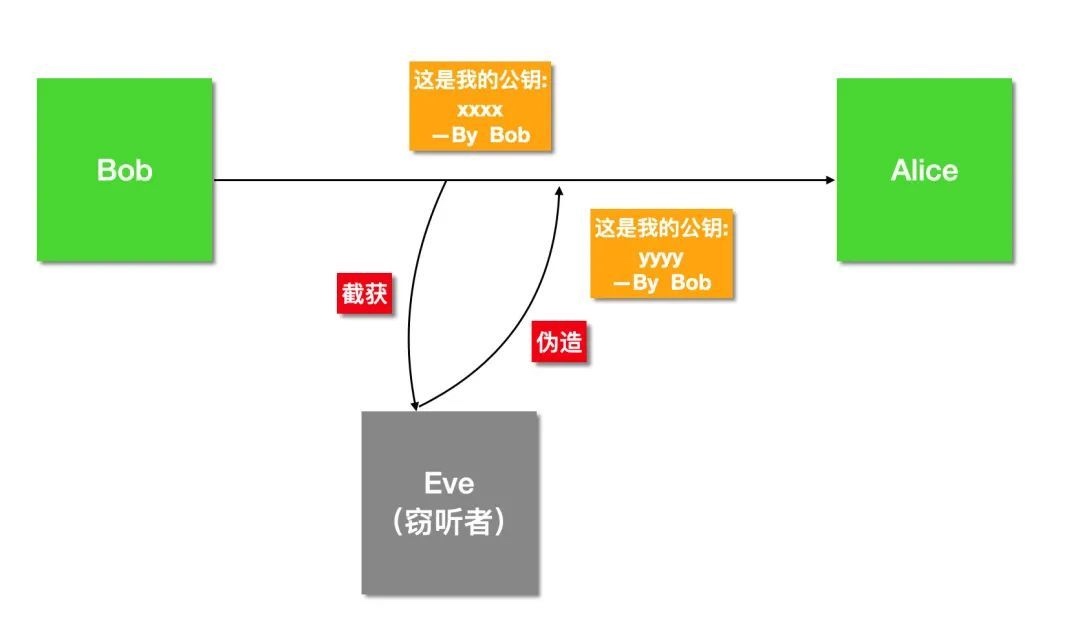
Bob 和 Alice 现在可以依赖于对称加密进行保密通信,也可以依赖于数字签名验证消息是否是对方发送的。
但是这一切的根基是建立在 Alice 持有的公钥确实是 Bob的,反之亦然。
Eve 如果将自己的公钥冒充 Bob 发送给 Alice,然后 Alice 保存了下来,那以后凡是 Bob 发送的消息,反而会验证签名失败,被当做冒充者。
数字证书
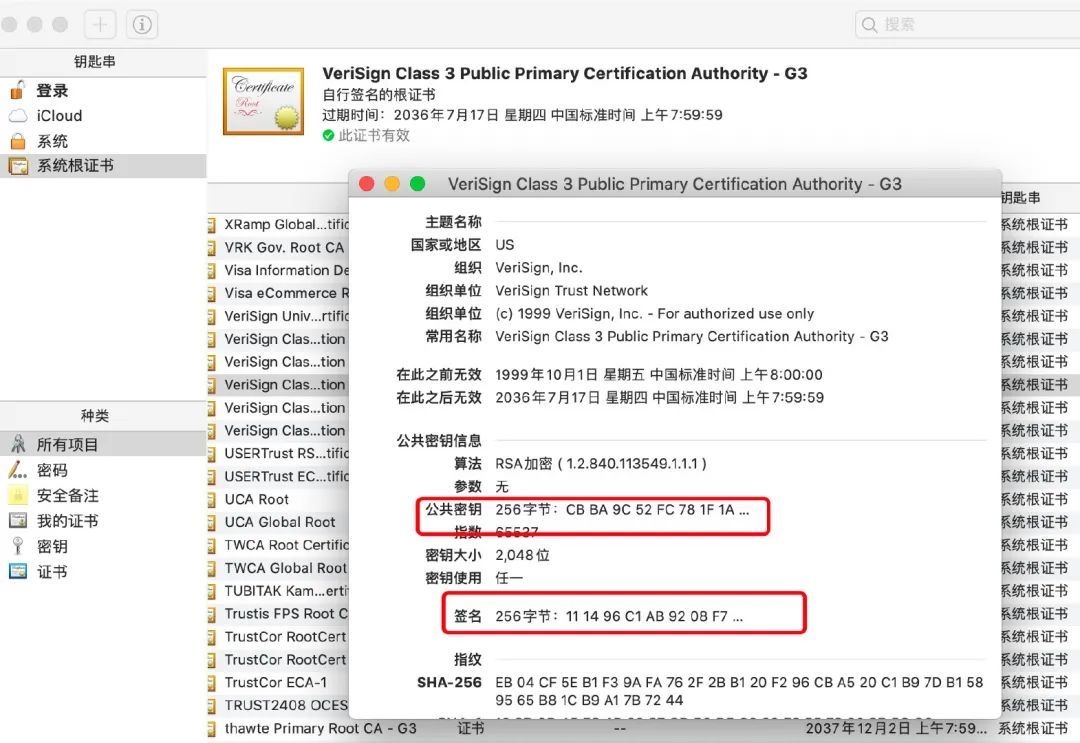
引入数字证书的目的是为了保证公钥不被篡改,即使被篡改了也能识别出来。
而防篡改的方法就是数字签名,但是这个签名不能我们自己做,原因说过了,因为我们的公钥还没分发出去,别人无法验证。
所以只能找可信的第三方来帮我们签名,即证书颁布机构(CA),CA 会将:证书的颁布机构、有效期、公钥、持有者(subject)等信息用 CA 的私钥进行签名。
并且将签名结果和这些信息放在一起,这就叫做「数字证书」。
收到 Bob 发过来的数字证书后,Alice 使用 CA 的公钥进行验证,验证通过即证明这确实是 Bob 证书,也就可以使用证书中包含的 Bob 的公钥,按照之前讨论的流程进行通信。
encryption
The purpose of encryption
- encryption
- encryption keys
- plaintext - The original data
- ciphertext - encrypted data
Symmetric and asymmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption uses a single encryption key. The same key is used to encrypt data and to decrypt data.
Asymmetric encryption uses two keys:: a public key (known to everyone) and a private key (known to one user only). Matching pairs (private and public keys) are generated by an encryption algorithm.