Chapter 1
Data Representation
1.01 Binary number system
二进制和十进制的来源
十进制的来源
人类计算使用十进制,可能是跟人类的手指有10根有关。数学来源于计数,最原始的方法就是数手指头。 亚里士多德称人类普遍使用十进制,只不过是绝大多数人生来就有10根手指这样一个解剖学事实的结果。
古罗马数字5进制
玛雅人的20进制
其他进制
二进制——最简单,但是使用起来较复杂
八进制——
十二进制——一年十二个月份,
十六进制——十六两合一斤
二十进制——玛雅人使用,手和脚一共有20根,来进行计数
二进制的来源
早期设计的机械计算装置中,使用的不是二进制,而是十进制或者其他进制,利用齿轮的不同位置表示不同的数值,这种计算装置可能更加接近人类的思想方式。比如说一个计算设备有十个齿轮,它们级连接起来,每一个齿轮有十格,小齿轮转一圈大齿轮走一格。这就是一个简单的十位十进制的数据表示设备了,可以表示0到999999999的数字。 配合其他的一些机械设备,这样一个简单的基于齿轮的装置就可以实现简单的十进制加减法了。
电子计算机出现以后,使用电子管来表示十种状态过于复杂,所以所有的电子计算机中只有两种基本的状态,开和关。
为什么要用二进制
- 电路中容易实现 :当计算机工作的时候,电路通电工作,于是每个输出端就有了电压。
- 用二进制表示数据具有抗干扰能力强,可靠性高等优点。因为每位数据只有高低两个状态,当受到一定程度的干扰时,仍能可靠地分辨出它是高还是低。
- 便于逻辑判断(是或非)。适合逻辑运算:逻辑代数是逻辑运算的理论依据,二进制只有两个数码,正好与逻辑代数中的“真”和“假”相吻合。
所有信息在计算机中都是二进制表达
The word 'Hello' is stored as the binary combination of 0100100001100101011011000110110001101111
1.02 Number Systems
Key Terms
- Data - numbers, symbols or alphanumeric characters in their raw format before processing.
- Analogue - this is the smooth stream of data that our senses process on a daily basis, such as a sound wave.
- Digital - data represented in the values 1 and 0 that a computer can process.
- Denary - a system of numbers with a base of 10.Each unit used increases by the power of 10
- Binary – a system of numbers with a base of 2. Each unit used increases by the power of 2.
Converting between denary and binary
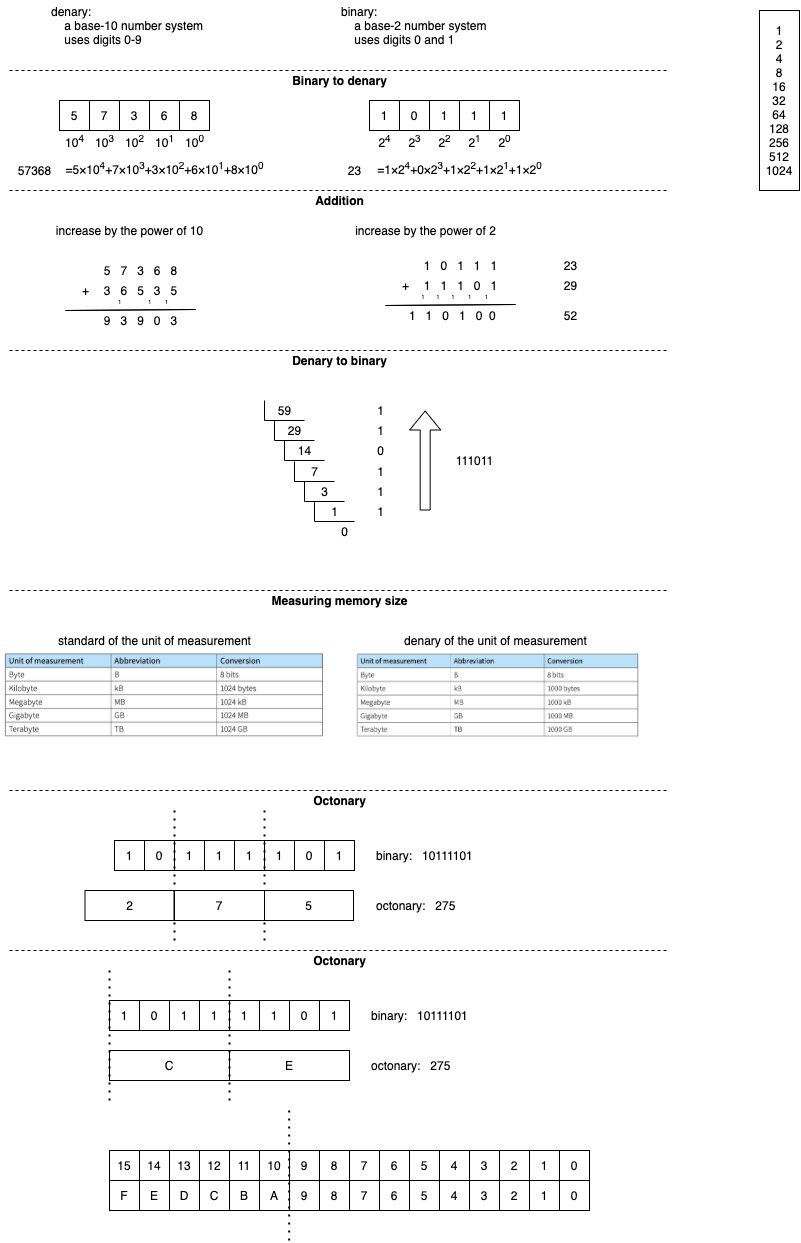
Overflow
overflow error is an indication that a number is too big to be stored in the computer using.

Logical binary shifts
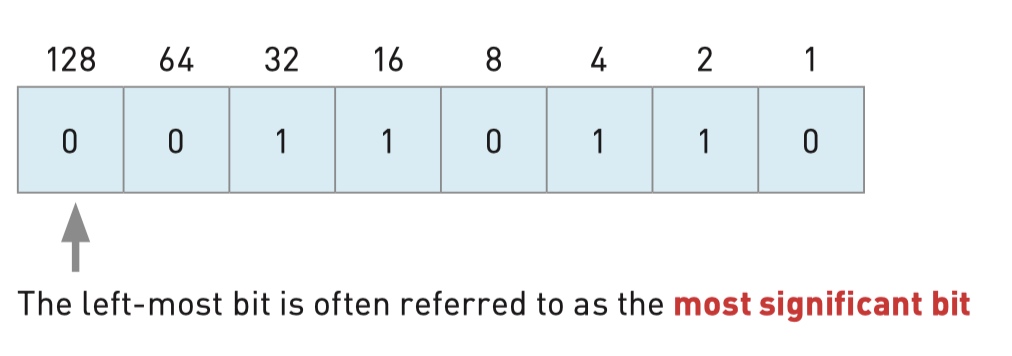
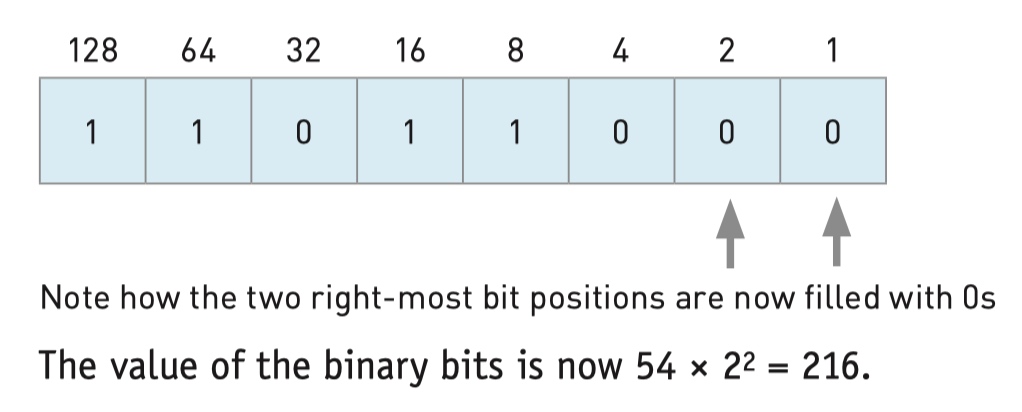
- Logical shifts involve shifting (moving) bits to the
- left (multiplying by 2 for each shift) or the
- right (dividing by 2 for each shift). If shifting to the left or right results in a loss of 1-bits, then this would result in an error.
One's complement
对于小学生来说,会做5-3,但是不会做3-5。 后续我们就引入了负数的概念
3-5=3+[-5] = [-2] 中括号的数代表“反码“
计算机的数字电路只有加法器,没有减法器。既然可以用反码来做减法,所以不需要单独来设计减法器
3 = [0_0000011] 5 = [0_0000101] 符号位负数 -5 = [1_0000101] 反码 -5 = [1_11111010]
3 +[-5] =[-2] [0_0000011]+[1_1111010]=[1_11111101]
为什么可以实现:
实际上反码可以理解为 -5 = [1_1111010] = 255 - 5
[3] + [-5] = 3 + 255 – 5 = 253 = 255 -2 = [-2]
[7] + [-5] = 7 + 255 – 5 = 255 + 2 = [2]
反码的问题:
[0_00000000] ~ +0 和 [1_11111111] ~ -0 所以存在两个0,这样在计算中是没有必要的
Two's complement
因为0 这个特殊的数字存在。0既不是正数也不是负数。
对于反码来说 正数 +0 ~ +127 负数 -127 ~ -0
所以会出现两个0:
[0_0000000] +0
[1_1111111] -0
但是对于计算机来说任何数字都只能有一个编码。所以把负数整体向后移动一位,这样范围就变成 -128 ~ -1 0 ~ 127。 将这个反码+1 称为补码
补码: 正数的补码保持不变 3 = [0_0000011]
负数先求反码,然后再加 1 - 5 = [1_1111010] + 1 = [1_1111011]
3 + [-5] = [-2] [0_0000011] + [1_1111011] = [11111110]
Binary coded decimal (depreciated)
This is useful in applications that require single denary digits to be stored or transmitted.
The BCD code uses a nibble to represent a denary digit.

1.03 Text, Sound and Images
Key Items
- character – text, numbers and symbols, for example each key on a keyboard.
ASCII Code
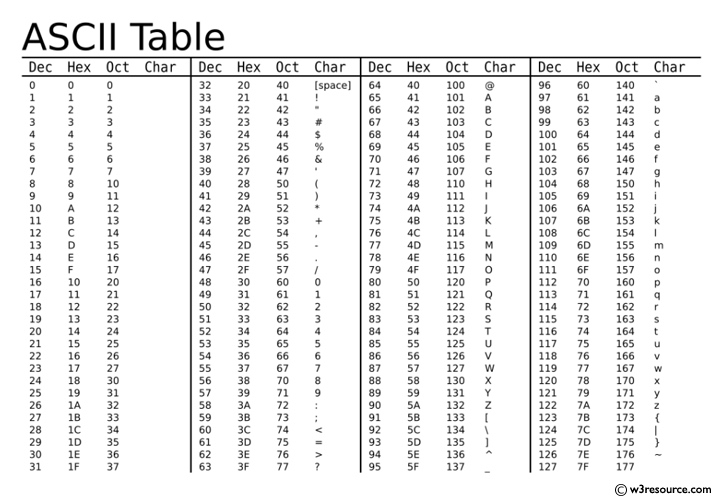
In AscII each character will take 1 byte of storage space as it is made up of 8 bits.
The 7-bit version of the code (often referred to as US ASCII) was standardised many years ago by ANSI (American National Standards Institute).
Unicode

In Unicode a character takes up 2 bytes as it is made up of 16 bits.
It should be noted that Unicode codes have been developed in tandem with the Universal Character Set (UCS) scheme, standardised as ISO/IEC 10646
Note that for the two-byte, three-byte and four-byte representations all continuing bytes have the two most significant bits set to 10.
编码集推荐阅读 -> 从ASCII码->Unicode->UTF-8历史变迁,及其差异
beyond 8-bit binary
Measuring memory size
- Byte B
- Kilobyte KB
- Megabyte MB
- Gigabyte GB
- Terabyte TB
- Petabyte PB
Using binary in computer registers
Register - small piece of memory where values can be held
A register is a small piece of memory built into the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer system where values and instructions are temporarily held.
- small in capacity
- extremely fast read and write rate
- data can be written to and read from a register much quicker than from primary memory or secondary storage
Uses of the hexadecimal system
Hexadecimal – a system of numbers with a base of 16. Each unit used increases by the power of 16.
Debug – finding and fixing problems and errors in a program.
Computers can not actually process hexadecimal, they convert it into binary before processing it.
Programmers work with hexadecimal as it is easier for humans to read than binary. Computers convert hexadecimal data into binary before processing it.
- Error codes
- Media Access Control (MAC) address
- Internet Protocol (IP) address
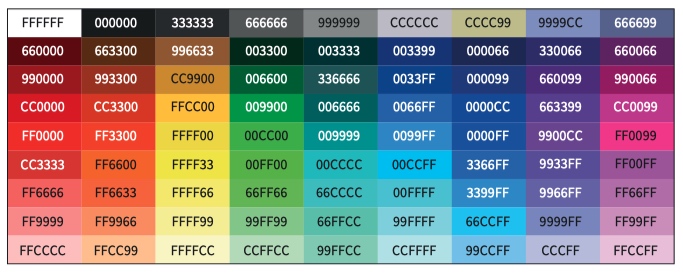
- Hypertext mark-up language (HTML) colour codes
html color
Mac Address
Media Access Control(MAC) address are 12-digit hexadecimal numbers that uniquely identify each different device in a network.
00-1B-6384-45-E6
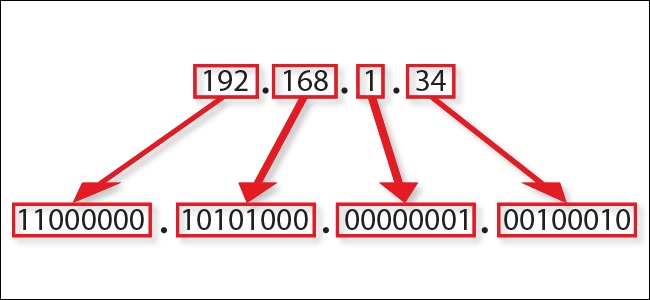
IP address
Text, numbers and symbols
ASCII

In AscII each character will take 1 byte of storage space as it is made up of 8 bits.
In Unicode a character takes up 2 bytes as it is made up of 16 bits.
UTF-8
Pictures
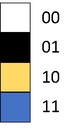
Image represented by a binary value. "bit-plane". 1-bit would give us 2 colors, 2-bits would give us 4 colors, 3-bits would give us 8 colors.
1-bit picture 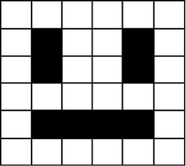
1-bit picture 
2-bits 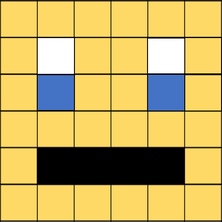
2-bits 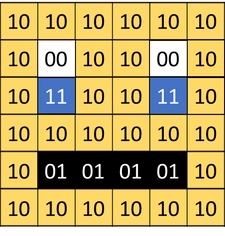
2-bits
- Color depth – how many bits represent each pixel
- Resolution - Width & Height (in pixels)
RGB color
256 colors 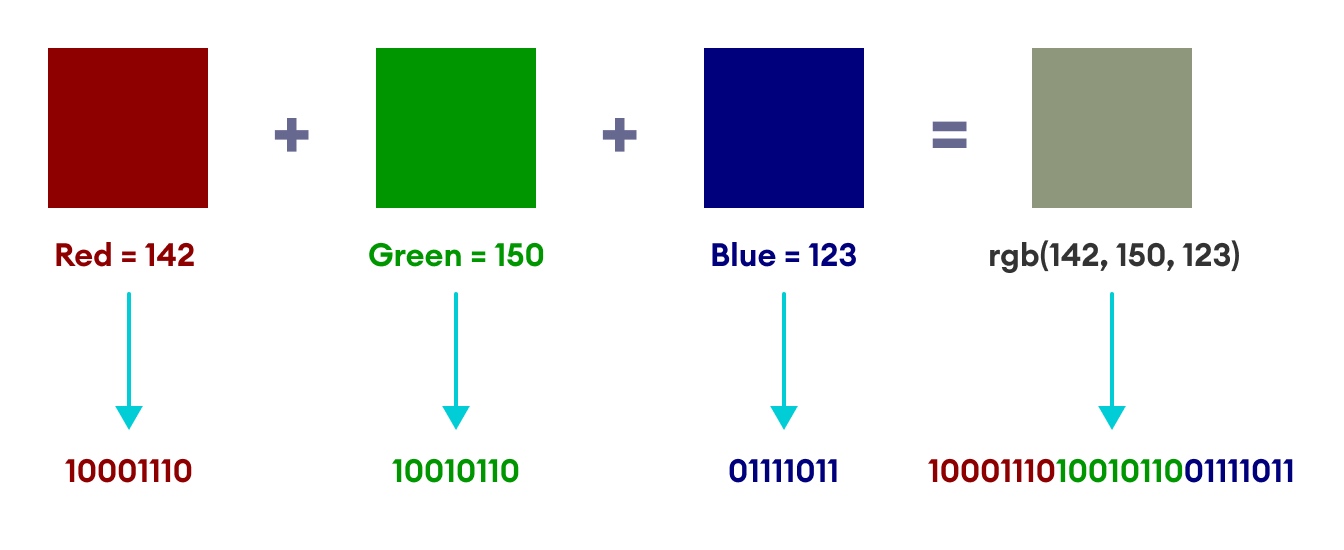
RGB and Binary 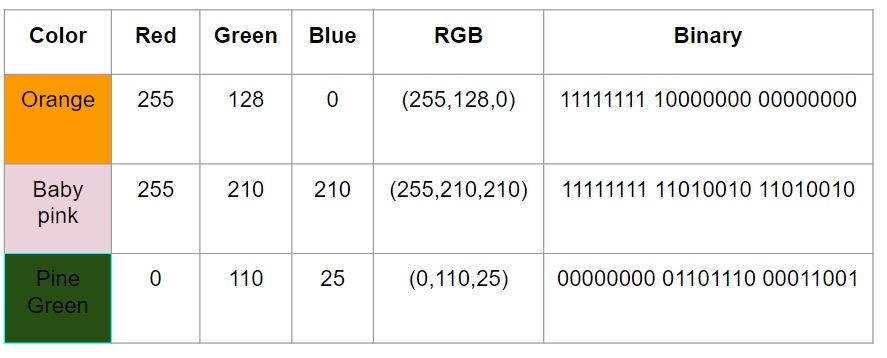
gray image 
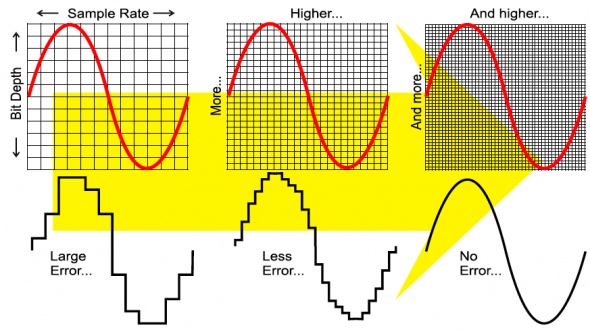
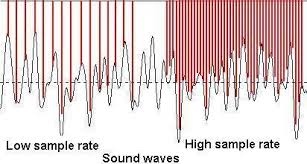
Sound
Calculation of file size
image file prefix::
image resolution (number of pixels) × colour depth (in bits)
image with pixel 4160*3120::
R ~ 8 bits, G ~ 8 bits, B ~ 8 bits
RGB ~ 3 Byte
image file size:: 4160 * 3120 * 3 Byte = 38,937,600 Byte / 1024 = 38025 KiB /1024 = 37.13 MiB
1.04 Data storage and file compression
key terms
- Algorithm - a step-by-step set of instructions
Data compression is done by using compression algorithms that manipulate the data.
feature::
- less storage space
- file will easier to transmit from one device to another
Measurement of data storage
decimal prefix
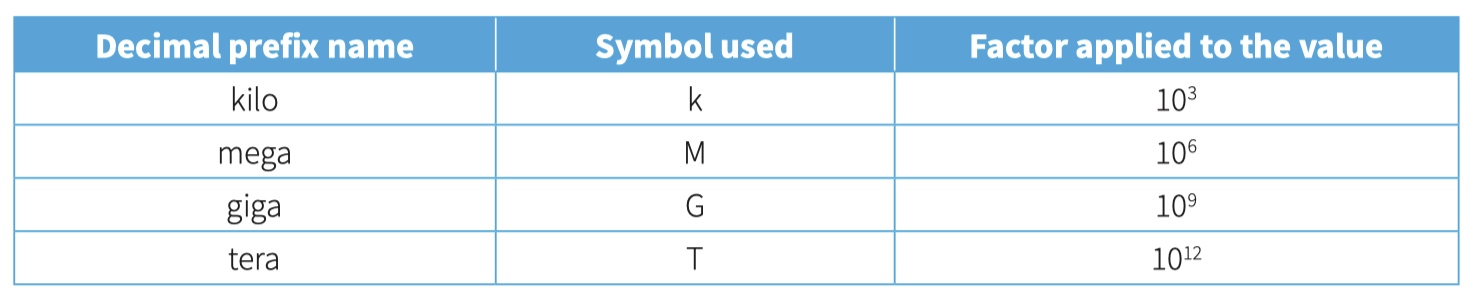
binary prefix

compression
Lossy compression
The data is removed permanently, so it is effectively ‘lost’. This way the size of the file is reduced.
mostly used for multimedia such as audio, video and image files
Lossless compression
Lossless refers to a method of compression that loses no data in the process.
the compressed data can be reversed to reconstruct the data file exactly as it was
Run length encoding(RLE)
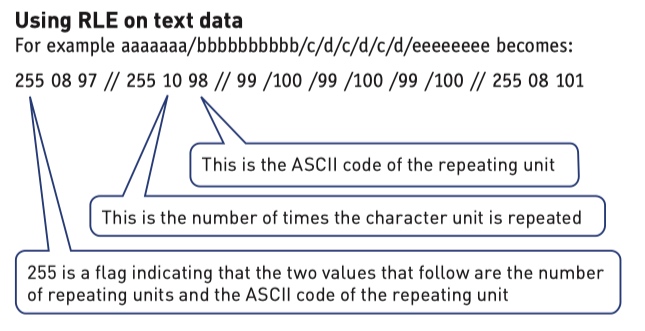
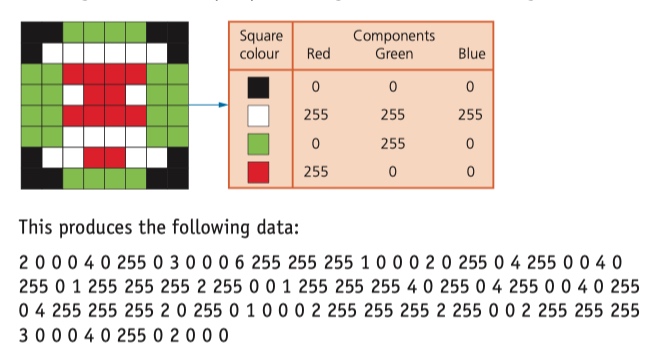
The original image (8 × 8 square) would need three bytes per square (to include all three RGB values). Therefore, the uncompressed file for this image is::
8 × 8 × 3 = 192 bytes.
The RLE code has 92 values, which means the compressed file will be 92 bytes in size.
example::
WHEN IT IS SNOWING HEAVILY LOOK OUTSIDE. LOOK OUTSIDE IT IS SNOWING HEAVILY.
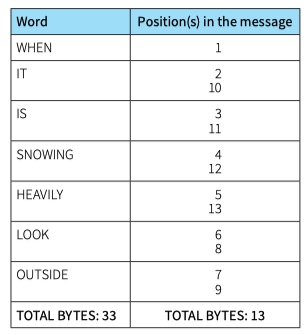
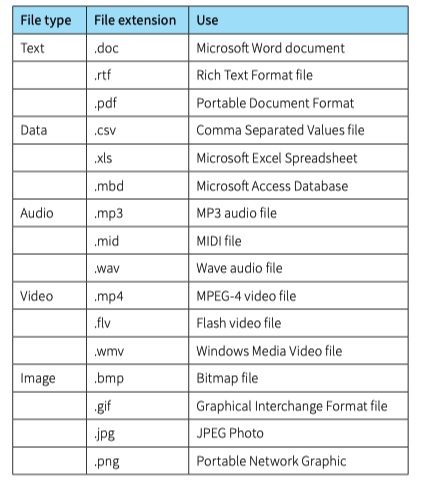
Image Format
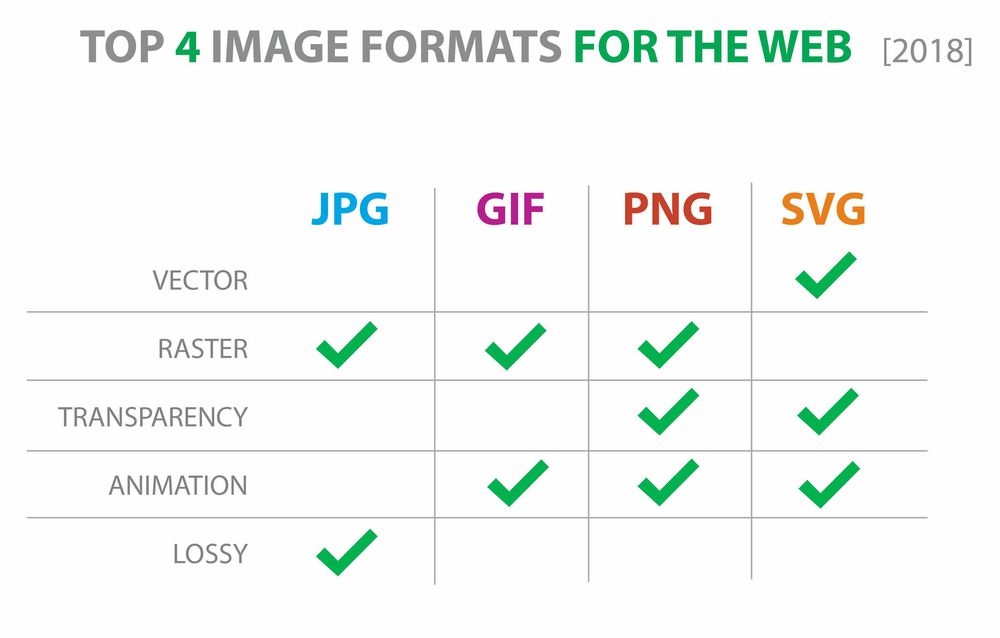
File formats
A file format is the method that we choose to store different data on a computer.